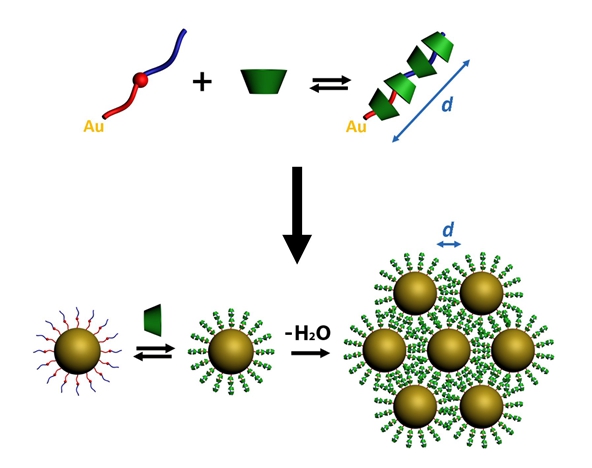
Amphiphilic nonionic ligands, synthesized with a fixed hydrophobic moiety formed by a thiolated alkyl chain and an aromatic ring, and with a hydrophilic tail composed of a variable number of oxyethylene units, were used to functionalize spherical gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) in water. Steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence measurements of the AuNPs in the presence of α-cyclodextrin (α-CD) revealed the formation of supramolecular complexes between the ligand and macrocycle at the surface of the nanocrystals.
The addition of α-CD induced the formation of inclusion complexes with a high apparent binding constant that decreased with the increasing oxyethylene chain length. The formation of polyrotaxanes at the surface of AuNPs, in which many α-CDs are trapped as hosts on the long and linear ligands, was demonstrated by the formation of large and homogeneous arrays of self-assembled AuNPs with hexagonal close packing, where the interparticle distance increased with the length of the oxyethylene chain.
The estimated number of α-CDs per polyrotaxane suggests a high rigidization of the ligand upon complexation, allowing for nearly perfect control of the interparticle distance in the arrays. This degree of supramolecular control was extended to arrays formed by AuNPs stabilized with polyethylene glycol and even to binary arrays. Electromagnetic simulations showed that the enhancement and distribution of the electric field can be finely controlled in these plasmonic arrays.
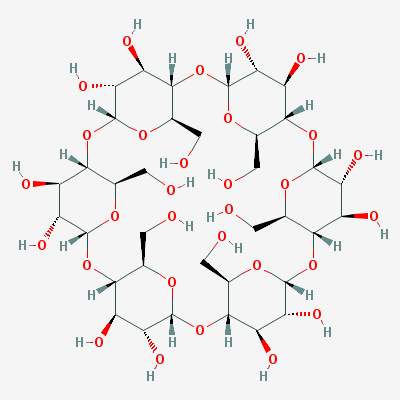
Alpha-Cyclodextrin (synonyms: cyclohexaamylose, cyclomaltohexaose, alpha-Schar-dinger dextrin) is a non-reducing cyclic saccharide comprised of six glucose units linked by alpha-1, 4 bonds.
It is produced by the action of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (CGTase, EC 2.4.1.19) on hydrolysed starch syrups at neutral pH (6.0–7.0) and moderate temperature (35–40°C).
The annular (or doughnut-shaped) structure of alpha-cyclodextrin provides a hydrophobic cavity that allows formation of inclusion complexes with a variety of non-polar organic molecules of appropriate size.
The cavity of alpha-cyclodextrin is less than beta-cyclodextrin, so it is used to allow formation of inclusion complexes with little molecules, and the situation that needs high solubility of cyclodextrin.
The hydrophilic nature of the outer surface of the cyclic structure makes alpha-cyclodextrin water-soluble.
Other name: Cyclohexapentylose
CAS Registry Number: 10016-20-3
MF: C36H60O30
MW: 972.84
EINECS NO.: 233-007-4
Appearance: white crystalline or powder
Assay:99%min
Application:
Alpha cyclodextrin is widely used in the drugs, food,flavor and cosmetics. Alpha cyclodextrin is also widely used in the field of pesticide and adjusting the metabolization of the crop and increasing the quantity of the crop. Especially the cyclodextrin and its ramification which developed by these years,some of cyclodextrins are the important solutizer,stablizer, releaser or the assist materials of the Entericcoated drugs, some of cyclodextrins are the materials of organic synthetical macromolecular stuff.
Function:
a.Increase the stability of the material:Prevent volatilization, prevent sublimation; Anti-oxidation; Prevent optothermal decomposition; Anti chemical decomposition; Extend the period of validity of the material.
b.Increase the material solubility and bioavailability.
c.Through the formation of inclusion complex to achieve effective cover excitant odour.
d.Liquid drug into solid state.
e.To prevent drug - drug, drug - interaction between additive.
f.Reduce side effects
Alpha Cyclodextrin Cyclohexapentylose,α-cyclodextrin
Zhiyuan Biotchnology , http://www.zycydextrin.com